- Description
- Warranty Information
- Hardware Specifications
- How to Install Laptop RAM?
- How to Check Laptop RAM?
- FAQs
XUM 32GB Laptop Memory RAM 2666 Mhz DDR4 PC4-21300 SODIMM Non-ECC Unbuffered 260 Pin 1.2V
Upgrade Your Laptop's Memory with 32GB DDR4 PC4-21300 2666MHz SODIMM Improve your laptop's performance with our DDR4 PC4-21300 2666 MHz 260-pin SODIMM. Tailored for SODIMM laptop memory, this module features 260 gold connectors for secure and reliable connectivity. Operating on the PC4-21300/DDR4 bus type, it achieves a data transfer rate of 2666 MHz.
The non-ECC unbuffered design ensures stability and reliability, delivering a smooth computing experience. With a voltage range of 1.2V, this memory module balances performance and power efficiency.
Compatible with a wide range of laptop models, including but not limited to:
- Dell Inspiron Series
- HP Pavilion Series
- Lenovo ThinkPad Series
- ASUS ZenBook Series
- Acer Aspire Series
Whether you're a casual user looking to speed up everyday tasks or a professional handling resource-intensive applications, our 32GB DDR4 Laptop Memory RAM module is the perfect solution. Unlock the full potential of your laptop and experience smoother performance across various computing tasks.
Upgrade today and enjoy a noticeable boost in your laptop's speed and responsiveness, whether you're gaming, streaming, or working on multimedia projects. With easy installation and dependable performance, XUM DDR4 Laptop Memory RAM module is your key to unlocking a more efficient computing experience.
-

- Bandwidth:
- 21300 MB/s
-

- Bus Speed:
- PC4-21300 (DDR4-2666)
-

- Capacity:
- 32GB (1 x 32GB)
-
- CAS:
- CL19
-

- Clock Speed:
- 2666Mhz
-

- Compatibility:
- DDR4 Motherboards, Laptops
-
- Condition:
- New
-

- Data Integrity:
- Non-ECC Unbuffered
-

- Form Factor:
- SODIMM (Small Outline Dual In-Line Memory Module)
-

- Manufacturer:
- XUM
-

- Memory Type:
- DDR4 SDRAM
-

- Number of Pins:
- 260 Pin
-
- Rank:
- 2R
-
- Voltage:
- 1.2
How to Install Memory RAM in Your Laptop: Step by Step
Step 1
-
Shut Down Your Laptop:
Make sure to properly shut down your laptop through the operating system.
-
Unplug the Power Cable:
Remove any cables connected to the laptop, including the power cable.
-
Remove the Battery:
If your laptop has a removable battery, take it out.
-
Discharge Residual Power:
Press and hold the power button for 3-5 seconds to discharge any residual electricity.

Step 2
-
Open the Laptop Case:
Consult the owner’s manual for instructions on how to open your specific laptop case.
-
Ground Yourself:
Touch an unpainted metal surface to discharge static electricity. Better yet, wear an anti-static wrist strap attached to a grounded object.
-
Locate the RAM Slots:
Open the case and locate the RAM slots on the motherboard. Note that on laptops, memory slots can be located under the keyboard or the back casing.
-
Remove Existing RAM (if applicable):
Press down on the clips at the ends of the RAM slot.
Gently remove the existing RAM module by holding the edges.
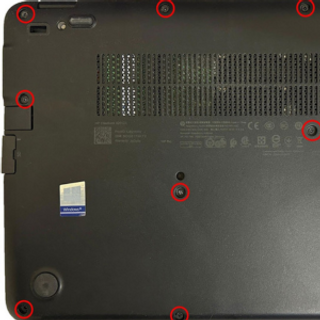
Step 3
-
Install New RAM:
Hold the new RAM module by the edges.
Align the notch on the module with the key in the slot.
Firmly push the module in at a 45° angle, then push down until the clips on the side of the slot snap into place. Only a thin portion of the gold pins should be visible.
-
Reassemble the Laptop:
Once all the RAM modules are securely installed, reassemble your laptop and replace the battery if it was removed.
-
Reconnect Cables:
Plug in the power cable and any other cables you disconnected.

Step 4
-
Power On and Test:
Turn on your laptop. It’s recommended to enter the BIOS to ensure the new RAM is recognized and running at the correct speed
-
Check System Properties:
Once your laptop has booted into the operating system, check the system properties to confirm that the new RAM is detected and usable
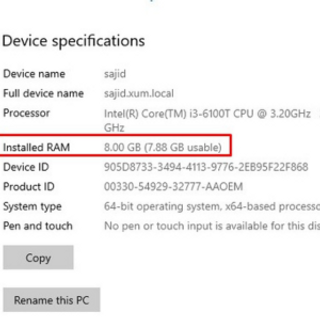
Post-Installation
- Enjoy Your Upgraded Laptop: You should now notice improved performance, especially when running memory-intensive applications.
- Remember to handle the RAM modules carefully and avoid touching the gold connectors. Always work in a clean, static-free environment, and if you’re unsure about the process, seek professional assistance.
Happy upgrading!
How to Check Memory RAM in Your Laptop
Step 1: Identify Installed Memory
- Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialogue box.
- Type msinfo32 and press Enter. That opens the System Information window.
- In the left pane, navigate to System Summary. On the right side, complete details about your installed memory, including the total installed physical memory (RAM).
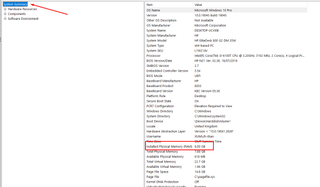
Step 2: Using Command Prompt to Convert Memory Size to GB
- Open Command Prompt by pressing the Windows key + R and typing cmd into the search bar.
- Type the following command: In the Command Prompt window, wmic memorychip get Capacity Press Enter. This command will show the capacity of each memory module in kilobytes (KB).
- To convert KB to GB, divide the capacity by 1,048,576 (1024 * 1024).
- For example, if the capacity is displayed as 4294967296 KB, the calculation would be 4294967296 KB / 1048576 = 4096 GB (for each memory module). Repeat this calculation for each memory module listed to determine the total memory size in GB.
Step 3: Maximum RAM Capacity
- Press the Windows Key + R, type cmd, then press Enter.
- In the command prompt, type wmic memphysical get maxcapacity, then press Enter.
- The result will be displayed in Kilobytes. Convert this to Gigabytes by dividing by (1024) twice.
- For example, calculate the maximum RAM capacity for a computer that supports up to 8GB: 10248388608KB = 8192MB, 10248192MB = 8GB. Thus, the maximum memory capacity is approximately 8 GB.
Step 4: RAM Slot Information Through Command Prompt
- Press the Windows Key + R to open the Run dialog box.
- Type cmd, then press Enter to launch the Command Prompt.
- In the Command Prompt window, type: wmic Memphysical get MemoryDevices, then press Enter.
- The number displayed represents the total number of RAM slots on your computer. For example, if it shows 2, your computer has two slots.
- To determine the maximum capacity per slot, divide the maximum RAM by the number of slots. For example, if your system has a maximum capacity of 8 GB and 2 slots, each slot supports up to 4 GB.
Alternate way Slot Information Through Task Manager
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc together to directly open the Task Manager.
- Click on the Performance tab in the Task Manager window.
- In the left pane, click on memory. This will display information about your system memory usage.
- Look for the Slots Used field under the Memory section. This indicates the number of memory slots currently in use.
Step 5: To identify the required generation of RAM:
- Open Task Manager with Ctrl + Shift + Esc or right-clicking the start button.
- Navigate to the Performance tab to find the RAM generation (e.g. DDR3, DDR4). RAM generations are not interchangeable.
Step 6: Check Memory Speed
- In the same Memory section of the System Information window look for the Speed field.
- The speed will be listed in megahertz (MHz) and indicates the frequency at which the memory operates.
Step 7: System Memory Support
- Option 1: Using Command Prompt
- Press the Windows Key + R to open the Run dialog box.
- To open the Command Prompt, type cmd, then press Enter.
- In the Command Prompt window, type: wmic os get OSArchitecture, then press Enter. This command will display whether your system is running a 32-bit or 64-bit version of Windows.
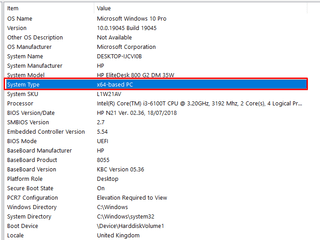
- Option 2: Check System Memory Support
- Press the Windows Key + R to open the Run dialog box.
- To open the System Information window, type msinfo32, then press Enter.
- In the System Information window, look for the System Type under the System Summary section. This will indicate whether your system is running a 32-bit or 64-bit version of Windows.
Based on your system's architecture, understand the following limitations:
- For 32-bit Windows: The maximum amount of RAM supported is typically around 4 GB, although this can vary depending on the specific version of Windows and any limitations imposed by hardware or software.
- For 64-bit Windows: The maximum amount of RAM supported varies depending on the specific edition of Windows. For example, Windows 10 Home supports a maximum of 128 GB of RAM, while Windows 10 Pro and Enterprise support up to 2 TB of RAM.
FAQs for Laptop Memory RAM
Laptop RAM (SO-DIMM) is smaller and has a different pin configuration compared to desktop RAM (DIMM).
While some laptops offer accessible RAM slots for upgrades, others may have non-upgradable, soldered RAM.
Modern laptops typically support anywhere from 8GB to 32GB or more, depending on the model and its motherboard capabilities.
If your laptop is running slow, you may want to upgrade the RAM or close unnecessary applications to free up memory.
If your system supports upgrades, consider increasing the RAM. Otherwise, optimize your current RAM by managing open applications and background processes.
Using multiple sticks can enable dual-channel mode, which can result in improved performance over a single stick.
We've got you covered with a detailed guide on our Product page. Look for the 'How to Check Laptop RAM' tab for all the information you need to check, install, and upgrade your laptop's memory.
Faster RAM can improve performance, but the difference may not be noticeable for everyday tasks.
These terms refer to the form factors of laptop RAM, with SODIMM being the standard size and MicroDIMM designed for ultra-compact devices.
It's technically possible, but matching RAM modules is recommended to ensure stability and performance, particularly for enabling dual-channel mode.
Upgrading your laptop's RAM can be a straightforward process. For a detailed, step-by-step guide, please visit our Product page and click on the 'How to Install Memory RAM in Your Laptop' tab. This guide will provide all the necessary instructions to ensure a successful RAM upgrade, from selecting the correct RAM to the actual installation process.
More RAM can reduce the need for page file usage, leading to faster application loading and better multitasking.
This depends on the warranty policy. Check your warranty terms before upgrading.


















